On February 12, President Donald Trump and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Administrator Lee Zeldin announced what they called the largest deregulation in U.S. history in the White House’s Roosevelt Room.
The EPA finalized a rule that removes the 2009 Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Endangerment Finding. The Obama administration created this finding, and it gave the federal government the legal authority to regulate greenhouse gas emissions under the Clean Air Act for more than a decade.
The new rule also removes all federal greenhouse gas standards for cars, trucks, and engines built from model year 2012 through 2027 and beyond. In addition, the EPA ended compliance credits tied to certain technologies, including start-stop systems.
In short, the administration rolled back the key rule that supported federal climate regulations on vehicles.
The Role of the 2009 Endangerment Finding
In 2009, the EPA said that six major greenhouse gases—including carbon dioxide—harm public health and the environment. The agency concluded that these gases drive climate change and damage air quality. That decision gave the federal government the authority to set emission limits for light-, medium-, and heavy-duty vehicles. It also supported climate rules for power plants and the oil and gas industry.
Because of this finding, the EPA introduced several greenhouse gas standards over the past decade. These rules shaped vehicle design, fuel economy targets, and broader climate policy across multiple sectors.
Why the EPA Repealed It Now
In 2025, the Trump administration began reviewing the 2009 decision. Officials argued that some of the science behind the finding was weaker than originally believed. They also said earlier climate projections were too pessimistic.
Now that the repeal is final, the EPA says it no longer has authority under Section 202(a) of the Clean Air Act to regulate greenhouse gases the way it did before. The agency believes Congress—not federal regulators—should decide major climate policy.
EPA leaders say this move restores a strict reading of the law and ends what they call regulatory overreach. Critics strongly disagree. Many scientists and public health experts argue that the repeal removes an important tool that protects Americans and helps address climate change.
Most importantly, the EPA estimates the final rule will save more than $1.3 trillion. It removes requirements for automakers to measure, report, certify, and comply with federal greenhouse gas standards. The agency says the rollback will lower vehicle prices, expand consumer choice, and reduce transportation costs for families and businesses.
Administrator Zeldin commented,
“The Endangerment Finding has been the source of 16 years of consumer choice restrictions and trillions of dollars in hidden costs for Americans. Referred to by some as the ‘Holy Grail’ of the ‘climate change religion,’ the Endangerment Finding is now eliminated. The Trump EPA is strictly following the letter of the law, returning commonsense to policy, delivering consumer choice to Americans and advancing the American Dream. As EPA Administrator, I am proud to deliver the single largest deregulatory action in U.S. history on behalf of American taxpayers and consumers. As an added bonus, the off-cycle credit for the almost universally despised start-stop feature on vehicles has been removed.”
U.S. Emissions Trends in 2025: Mixed Signals
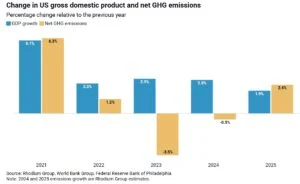
At a climate crossroads, the United States saw a rebound in greenhouse gas emissions in 2025 after years of overall decline. According to estimates from the Rhodium Group, total U.S. emissions rose about 2.4% in 2025, reaching roughly 5.9 billion tons of CO₂ equivalent—139 million tons higher than in 2024. This uptick ended a two‑year downward trend that had been driven by cleaner energy and transportation shifts.

Several factors pushed emissions higher: colder winter weather increased demand for heating; rising electricity demand from data centers and cryptocurrency mining boosted fossil fuel use; and higher natural gas prices led utilities to burn more coal. The power sector alone saw a 3.8% rise in emissions, while buildings’ emissions jumped 6.8%. Transportation emissions, the largest U.S. source, remained largely flat, increasing only modestly due to continued adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles.

Despite the 2025 increase, total emissions are still below pre‑pandemic levels and well under 2005 baselines—roughly 18% below 2005 levels—showing that long‑term trends toward decarbonization have not entirely reversed yet.
Preliminary sector data from Climate TRACE also indicates that U.S. emissions continued rising throughout 2025, adding more than 71 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent through the first three quarters of the year.
The EV Market in 2025: Growth and Slowdowns
In contrast to emissions trends, the U.S. electric vehicle (EV) market continued to grow in 2025, though the pace and dynamics evolved. EVs made notable gains in sales and market share, reflecting both consumer demand and industry transitions.
In the first quarter of 2025, nearly 300,000 battery‑electric vehicles were newly registered, marking over a 10% year‑over‑year increase. EVs accounted for about 7.5% of all new car registrations during that period.
By the third quarter, sales surged again. Cox Automotive reported that EV sales jumped nearly 30% year‑over‑year, pushing EV market share to a record 10.5% of total vehicle sales in Q3 2025—a milestone reflecting strong consumer uptake in several segments.



Even so, EV adoption remains far from dominating the U.S. market. Estimates show that electric vehicles comprised around 8–10% of total U.S. new car sales in 2025, with internal‑combustion engine vehicles still accounting for the large majority of the fleet.
Tesla remained the largest EV brand in the U.S. in 2025, holding about 46% market share, though this marked a slight decline from previous years. Rivals like Chevrolet and Hyundai grew their shares, reflecting broader model availability and shifting consumer preferences.
Market analysts also project that by 2025, the U.S. EV market’s size, sales, and technology focus will continue expanding—with battery‑electric vehicles expected to dominate EV segments. The broader EV market size had substantial growth in 2025, with further expansion expected toward the end of the decade.

Balancing Regulation, Consumer Choice, and Emissions Goals
EPA officials say that removing federal GHG standards and related compliance credits will lower vehicle costs by about $2,400 per car. This will ease financial pressure on families and businesses and give buyers more choice. The agency calls it a step toward restoring the American Dream, making transportation more affordable without high regulatory costs.
Supporters argue the rollback removes artificial mandates, letting automakers and consumers focus on market-driven solutions. The EPA also ended “off-cycle” credits, which allowed carmakers to meet emission targets with minor technology changes. Critics called these credits gimmicks with little real environmental benefit.
Litigation and Future Policy
Environmental groups, scientists, and several states sharply criticized the move. They warn that it weakens climate action, public health protections, and emission reductions. Many fear that removing these rules while emissions are rising could set back U.S. climate goals.
Legal challenges are expected, with lawsuits likely to block or reverse the repeal. As federal rules change, state policies, corporate commitments, and Congress may play a larger role. Some states have already set carbon standards and EV incentives, creating a patchwork of climate policies across the country.
In conclusion, the 2026 repeal of the GHG Endangerment Finding marks a major shift in U.S. climate policy. With emissions rising and clean technology markets evolving, the country faces tough choices about balancing economic growth, innovation, and climate risk. The coming years will be shaped by lawsuits, state leadership, private investments, and the global move toward low-carbon economies.