Allen L. Non-communicable disease funding. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(2):92.
Vos T, Lim S S, Abbafati C, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204–22.
Lehtisalo J, Rusanen M, Solomon A, Antikainen R, Laatikainen T, Peltonen M, et al. Effect of a multi-domain lifestyle intervention on cardiovascular risk in older people: the FINGER trial. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(21):2054–61.
Yoo JE, Han K, Shin DW, Jung W, Kim D, Lee CM, et al. Effect of smoking reduction, cessation, and resumption on cancer risk: a nationwide cohort study. Cancer. 2022;128(11):2126–37.
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(6):393–403.
Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association’s strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. 2010;121(4):586–613.
Sotos-Prieto M, Moreno-Franco B, Ordovás JM, León M, Casasnovas JA, Peñalvo JL. Design and development of an instrument to measure overall lifestyle habits for epidemiological research: the Mediterranean Lifestyle (MEDLIFE) index. Public Health Nutr. 2015;18(6):959–67.
Shams-White MM, Brockton NT, Mitrou P, Romaguera D, Brown S, Bender A, et al. Operationalizing the 2018 World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (WCRF/AICR) cancer prevention recommendations: a standardized scoring system. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1572.
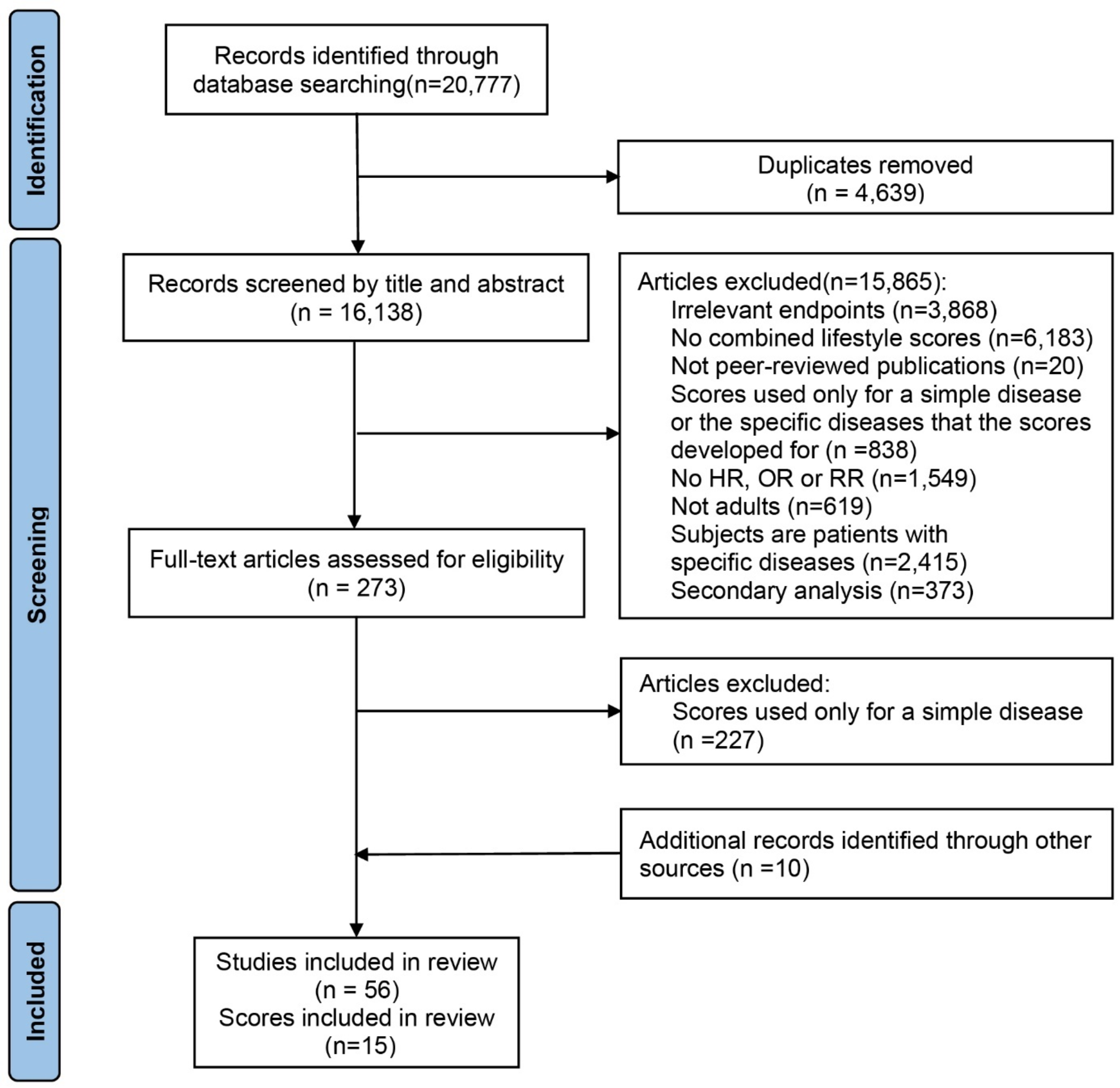
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Higgins JP, Morgan RL, Rooney AA, Taylor KW, Thayer KA, Silva RA, et al. A tool to assess risk of bias in non-randomized follow-up studies of exposure effects (ROBINS-E). Environ Int. 2024;186:108602.
Kurth T, Moore SC, Gaziano JM, Kase CS, Stampfer MJ, Berger K, et al. Healthy lifestyle and the risk of stroke in women. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(13):1403–9.
McKenzie F, Ferrari P, Freisling H, Chajès V, Rinaldi S, de Batlle J, et al. Healthy lifestyle and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal women in the European prospective investigation into Cancer and Nutrition cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(11):2640–8.
McKenzie F, Biessy C, Ferrari P, Freisling H, Rinaldi S, Chajès V, et al. Healthy lifestyle and risk of Cancer in the European prospective investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Cohort Study. Med (Baltim). 2016;95(16):e2850.
Arthur R, Kirsh VA, Kreiger N, Rohan T. A healthy lifestyle index and its association with risk of breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancer among Canadian women. Cancer Causes Control. 2018;29(6):485–93.
Arthur R, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Manson JE, Luo J, Snetselaar L, Hastert T, et al. The Combined Association of modifiable risk factors with breast Cancer risk in the women’s Health Initiative. Cancer Prev Res (Philadelphia Pa). 2018;11(6):317–26.
Arthur R, Brasky TM, Crane TE, Felix AS, Kaunitz AM, Shadyab AH, et al. Associations of a healthy Lifestyle Index with the risks of endometrial and ovarian Cancer among women in the women’s Health Initiative Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(2):261–73.
Naudin S, Viallon V, Hashim D, Freisling H, Jenab M, Weiderpass E, et al. Healthy lifestyle and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the EPIC study. Eur J Epidemiol. 2020;35(10):975–86.
Naudin S, Solans Margalef M, Saberi Hosnijeh F, Nieters A, Kyrø C, Tjønneland A, et al. Healthy lifestyle and the risk of lymphoma in the European prospective investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(6):1649–56.
Freisling H, Viallon V, Lennon H, Bagnardi V, Ricci C, Butterworth AS, et al. Lifestyle factors and risk of multimorbidity of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases: a multinational cohort study. BMC Med. 2020;18(1):5.
Chen SLF, Braaten T, Borch KB, Ferrari P, Sandanger TM, Nøst TH. Combined lifestyle behaviors and the incidence of Common Cancer types in the Norwegian women and Cancer Study (NOWAC). Clin Epidemiol. 2021;13:721–34.
Peila R, Coday M, Crane TE, Saquib N, Shadyab AH, Tabung FK, et al. Healthy lifestyle index and risk of pancreatic cancer in the women’s Health Initiative. Cancer Causes Control. 2022;33(5):737–47.
Peila R, Lane DS, Shadyab AH, Saquib N, Strickler HD, Manson JE, et al. Healthy lifestyle index and the risk of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in the women’s Health Initiative. Int J Cancer. 2022;151(4):526–38.
Meer R, van de Pol J, van den Brandt PA, Schouten LJ. The association of healthy lifestyle index score and the risk of renal cell cancer in the Netherlands cohort study. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):156.
Viallon V, Freisling H, Matta K, Nannsen A, Dahm CC, Tjønneland A, et al. On the use of the healthy lifestyle index to investigate specific disease outcomes. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):16330.
McCullough ML, Patel AV, Kushi LH, Patel R, Willett WC, Doyle C, et al. Following cancer prevention guidelines reduces risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prevention: Publication Am Association Cancer Res Cosponsored Am Soc Prev Oncol. 2011;20(6):1089–97.
Greenlee H, Strizich G, Lovasi GS, Kaplan RC, Biggs ML, Li CI, et al. Concordance with Prevention guidelines and subsequent Cancer, Cardiovascular Disease, and mortality: a longitudinal study of older adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2017;186(10):1168–79.
Li Y, Pan A, Wang DD, Liu X, Dhana K, Franco OH, et al. Impact of healthy lifestyle factors on life expectancies in the US Population. Circulation. 2018;138(4):345–55.
Lohse T, Faeh D, Bopp M, Rohrmann S. Adherence to the cancer prevention recommendations of the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research and mortality: a census-linked cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(3):678–85.
Mirizzi A, Aballay LR, Misciagna G, Caruso MG, Bonfiglio C, Sorino P, et al. Modified WCRF/AICR score and all-cause, digestive system, cardiovascular, cancer and other-cause-related mortality: a competing risk analysis of two cohort studies conducted in southern italy. Nutrients. 2021;13(11):4002.
Wang W, Fung TT, Wang M, Smith-Warner SA, Giovannucci EL, Tabung FK. Association of the Insulinemic potential of Diet and Lifestyle with risk of Digestive System cancers in men and women. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018;2(4):pky080.
Yang W, Sui J, Zhao L, Ma Y, Tabung FK, Simon TG, et al. Association of Inflammatory and Insulinemic Potential of Diet and Lifestyle with risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prevention: Publication Am Association Cancer Res Cosponsored Am Soc Prev Oncol. 2021;30(4):789–96.
Farhadnejad H, Mokhtari E, Teymoori F, Sohouli MH, Moslehi N, Mirmiran P, et al. Association of the insulinemic potential of diet and lifestyle with risk of diabetes incident in Tehranian adults: a population based cohort study. Nutr J. 2021;20(1):39.
Yue Y, Hur J, Cao Y, Tabung FK, Wang M, Wu K, et al. Prospective evaluation of dietary and lifestyle pattern indices with risk of colorectal cancer in a cohort of younger women. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(6):778–86.
Kim J, Lee J, Oh JH, Chang HJ, Sohn DK, Shin A et al. Interactive effect of the empirical lifestyle index for insulin resistance with the common genetic susceptibility locus rs2423279 for colorectal cancer. Br J Nutr 2022:1–11.
Mokhtari E, Jamshidi S, Daftari G, Farhadnejad H, Teymoori F, Momeni SA, et al. The relationship between the insulinemic potential of diet and lifestyle and risk of breast cancer: a case-control study among Iranian adult women. Archives Public Health = Archives belges de sante Publique. 2023;81(1):4.
Sicahni PH, Makhtoomi M, Leilami K, Shateri Z, Mohammadi F, Nouri M, et al. Dietary and lifestyle indices for hyperinsulinemia and colorectal cancer risk: a case-control study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023;23(1):434.
Omrani M, Hosseinzadeh M, Shab Bidar S, Mirzaei M, Teymoori F, Nadjarzadeh A, et al. Insulinaemic potential of diet and lifestyle and risk of type 2 diabetes in the Iranian adults: result from Yazd health study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023;23(1):136.
Teymoori F, Mokhtari E, Farhadnejad H, Mirmiran P, Rad HA, Azizi F. The dietary and lifestyle indices of insulin resistance are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular diseases: a prospective study among an Iranian adult population. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022;32(9):2216–26.
Byrd DA, Judd SE, Flanders WD, Hartman TJ, Fedirko V, Agurs-Collins T, et al. Associations of Novel Dietary and Lifestyle inflammation scores with Incident Colorectal Cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020;4(3):pkaa009.
Teymoori F, Farhadnejad H, Mokhtari E, Sohouli MH, Moslehi N, Mirmiran P, et al. Dietary and lifestyle inflammatory scores and risk of incident diabetes: a prospective cohort among participants of Tehran lipid and glucose study. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1293.
Li Z, Gao Y, Byrd DA, Gibbs DC, Prizment AE, Lazovich D, et al. Novel dietary and lifestyle inflammation scores directly Associated with All-Cause, All-Cancer, and all-Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Risks among women. J Nutr. 2021;151(4):930–9.
Gao Y, Byrd DA, Prizment A, Lazovich D, Bostick RM. Associations of Novel Lifestyle- and whole foods-based inflammation scores with Incident Colorectal Cancer among women. Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(4):1356–69.
Troeschel AN, Byrd DA, Judd S, Flanders WD, Bostick RM. Associations of dietary and lifestyle inflammation scores with mortality due to CVD, cancer, and all causes among black and white American men and women. Br J Nutr. 2023;129(3):523–34.
Lee HA, Park H, Park B. Genetic predisposition, lifestyle inflammation score, food-based dietary inflammatory index, and the risk for incident diabetes: findings from the KoGES data. Nutr Metabolism Cardiovasc Dis. 2024;34(3):642–50.
Sohouli MH, Hadizadeh M, Mardali F, Sanati V, da Silva Magalhães EI, Zarrati M. Association between novel dietary and lifestyle inflammation indices with risk of breast cancer (BrCa): a case-control study. Nutr J. 2022;21(1):14.
Jun S, Lee J, Oh JH, Chang HJ, Sohn DK, Shin A, et al. Association of the inflammatory balance of diet and lifestyle with colorectal cancer among Korean adults: a case-control study. Annals Nutr Metabolism. 2023;79:721.
Bakhshimoghaddam F, Jafarirad S, Maraghi E, Ghorat F. Association of dietary and lifestyle inflammation score with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiometabolic risk factors in Iranian adults: Sabzevar Persian Cohort Study. Br J Nutr. 2024;131(3):521–30.
Hosseinzadeh M, Saber N, Bidar SS, Hashemi S, Teymoori F, Mirzaei M, et al. Association of dietary and lifestyle inflammatory indices with type 2 diabetes risk in Iranian adults. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024;24(1):131.
Meng L, Maskarinec G, Lee J, Kolonel LN. Lifestyle factors and chronic diseases: application of a composite risk index. Prev Med. 1999;29(4):296–304.
Khaw KT, Wareham N, Bingham S, Welch A, Luben R, Day N. Combined impact of health behaviours and mortality in men and women: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. PLoS Med. 2008;5(1):e12.
Myint PK, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Bingham SA, Khaw KT. Combined effect of health behaviours and risk of first ever stroke in 20,040 men and women over 11 years’ follow-up in Norfolk cohort of European prospective investigation of Cancer (EPIC Norfolk): prospective population study. BMJ. 2009;338:b349.
Ogunmoroti O, Allen NB, Cushman M, Michos ED, Rundek T, Rana JS et al. Association Between Life’s Simple 7 and Noncardiovascular Disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Association 2016, 5(10).
Lau ES, Paniagua SM, Liu E, Jovani M, Li SX, Takvorian K, et al. Cardiovascular Risk factors are Associated with Future Cancer. JACC CardioOncol. 2021;3(1):48–58.
Han L, You D, Ma W, Astell-Burt T, Feng X, Duan S, et al. National Trends in American Heart Association Revised Life’s simple 7 Metrics Associated with Risk of Mortality among US adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(10):e1913131.
Fretts AM, Howard BV, McKnight B, Duncan GE, Beresford SA, Mete M, et al. Life’s simple 7 and incidence of diabetes among American indians: the strong Heart Family Study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(8):2240–5.
Plante TB, Koh I, Judd SE, Howard G, Howard VJ, Zakai NA, et al. Life’s simple 7 and Incident Hypertension: the REGARDS Study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(19):e016482.
Rasmussen-Torvik LJ, Shay CM, Abramson JG, Friedrich CA, Nettleton JA, Prizment AE, et al. Ideal cardiovascular health is inversely associated with incident cancer: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Circulation. 2013;127(12):1270–5.
Zhang J, Yu H, Huang T, Huang N, Liang H. Importance of ideal cardiovascular health metrics in the risk of colorectal cancer among people aged 50 years or older: a UK Biobank cohort study. BMJ open. 2022;12(5):e059642.
Yu YT, Sun Y, Yu YF, Wang YY, Chen C, Tan X, et al. Life’s essential 8 and risk of non-communicable chronic diseases: outcome-wide analyses. Chin Med J. 2024;137(13):1553–62.
Peng Y, Wang P, Du H, Liu F, Wang X, Si C et al. Cardiovascular health, polygenic risk score, and cancer risk: a prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 2024.
Hershey MS, Fernandez-Montero A, Sotos-Prieto M, Kales S, Gea A, Ruiz-Estigarribia L, et al. The Association between the Mediterranean Lifestyle Index and all-cause mortality in the Seguimiento Universidad De Navarra Cohort. Am J Prev Med. 2020;59(6):e239–48.
Sotos-Prieto M, Ortolá R, Ruiz-Canela M, Garcia-Esquinas E, Martínez-Gómez D, Lopez-Garcia E, et al. Association between the Mediterranean lifestyle, metabolic syndrome and mortality: a whole-country cohort in Spain. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021;20(1):5.
Mata-Fernández A, Hershey MS, Pastrana-Delgado JC, Sotos-Prieto M, Ruiz-Canela M, Kales SN, et al. A mediterranean lifestyle reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra (SUN) cohort. Nutr, Metab, Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;31(6):1728–37.
Maroto-Rodriguez J, Ortolá R, Carballo-Casla A, Iriarte-Campo V, Salinero-Fort M, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, et al. Association between a mediterranean lifestyle and type 2 diabetes incidence: a prospective UK biobank study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1):271.
Maroto-Rodriguez J, Delgado-Velandia M, Ortolá R, Perez-Cornago A, Kales SN, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, et al. Association of a Mediterranean Lifestyle with all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a prospective study from the UK Biobank. Mayo Clin Proc. 2024;99(4):551–63.
Meng L, Maskarinec G, Lee J, Kolonel LNJP. Lifestyle factors and chronic diseases: application of a composite risk index. 1999, 29(4):296–304.
Myint PK, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Bingham SA, Khaw K-TJB. Combined effect of health behaviours and risk of first ever stroke in 20 040 men and women over 11 years’ follow-up in Norfolk cohort of European prospective investigation of Cancer (EPIC Norfolk): prospective population study. 2009, 338.
Khaw K-T, Wareham N, Bingham S, Welch A, Luben R. Day NJPm: combined impact of health behaviours and mortality in men and women: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. 2008, 5(1):e12.
Zhang Y, Pan XF, Chen J, Xia L, Cao A, Zhang Y, et al. Combined lifestyle factors and risk of incident type 2 diabetes and prognosis among individuals with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetologia. 2020;63(1):21–33.
Li G, Zhang P, Wang J, An Y, Gong Q, Gregg EW, et al. Cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality, and diabetes incidence after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance in the Da Qing diabetes Prevention Study: a 23-year follow-up study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(6):474–80.
Gong Q, Zhang P, Wang J, Ma J, An Y, Chen Y, et al. Morbidity and mortality after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance: 30-year results of the Da Qing diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(6):452–61.
Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Fu S, Conjeevaram HS, Su GL, Lok AS. Alcohol, tobacco and obesity are synergistic risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2005;42(2):218–24.
Talamini R, Bosetti C, La Vecchia C, Dal Maso L, Levi F, Bidoli E, et al. Combined effect of tobacco and alcohol on laryngeal cancer risk: a case-control study. Cancer Causes Control. 2002;13(10):957–64.
Xu X, Mishra GD, Dobson AJ, Jones M. Progression of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke multimorbidity in middle-aged women: a 20-year cohort study. PLoS Med. 2018;15(3):e1002516.
Koene RJ, Prizment AE, Blaes A, Konety SH. Shared Risk factors in Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Circulation. 2016;133(11):1104–14.
Meijers WC, de Boer RA. Common risk factors for heart failure and cancer. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115(5):844–53.
Genkinger JM, Kitahara CM, Bernstein L, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Brotzman M, Elena JW, et al. Central adiposity, obesity during early adulthood, and pancreatic cancer mortality in a pooled analysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(11):2257–66.
Harvie M, Hooper L, Howell AH. Central obesity and breast cancer risk: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2003;4(3):157–73.
Freuer D, Linseisen J, O’Mara TA, Leitzmann M, Baurecht H, Baumeister SE, et al. Body fat distribution and risk of breast, endometrial, and ovarian cancer: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. Cancers. 2021;13(20):5053.
Ding J, Chen X, Bao K, Yang J, Liu N, Huang W, et al. Assessing different anthropometric indices and their optimal cutoffs for prediction of type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in asians: the Jinchang Cohort Study. J Diabetes. 2020;12(5):372–84.
Appropriate body-mass. Index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet (London England). 2004;363(9403):157–63.