Fashion trend forecasting helps companies predict which clothes will be popular in upcoming seasons. Traditionally, this has relied on experts’ intuition, experience and creativity. More recently, big-data analysis has been incorporated, offering deeper insights into consumer behavior. However, such methods pose technical barriers and remain out of reach for fashion students or small brands.
Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) can balance the scales. Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have made big data analysis readily available to the public.
LLMs draw from vast societal and cultural data and can potentially be used for predicting fashion trends. However, given their current limitations, such as hallucinations and factual errors, it is imperative to verify their suitability and to develop structured prediction methods.
In a new study, Assistant Professor Yoon Kyung Lee and Master’s student Chaehi Ryu, from the Department of Clothing and Textiles at Pusan National University, South Korea, developed a new approach for predicting fashion trends using ChatGPT.
“Rather than simply asking ‘What fashion will be popular in the future?’, we designed a systematic strategy for prompting the AI for more specific and consistent answers,” explains Dr. Lee. “We also compared ChatGPT’s predictions to an actual trend agency’s report.”
Their findings are published in the Clothing and Textiles Research Journal.
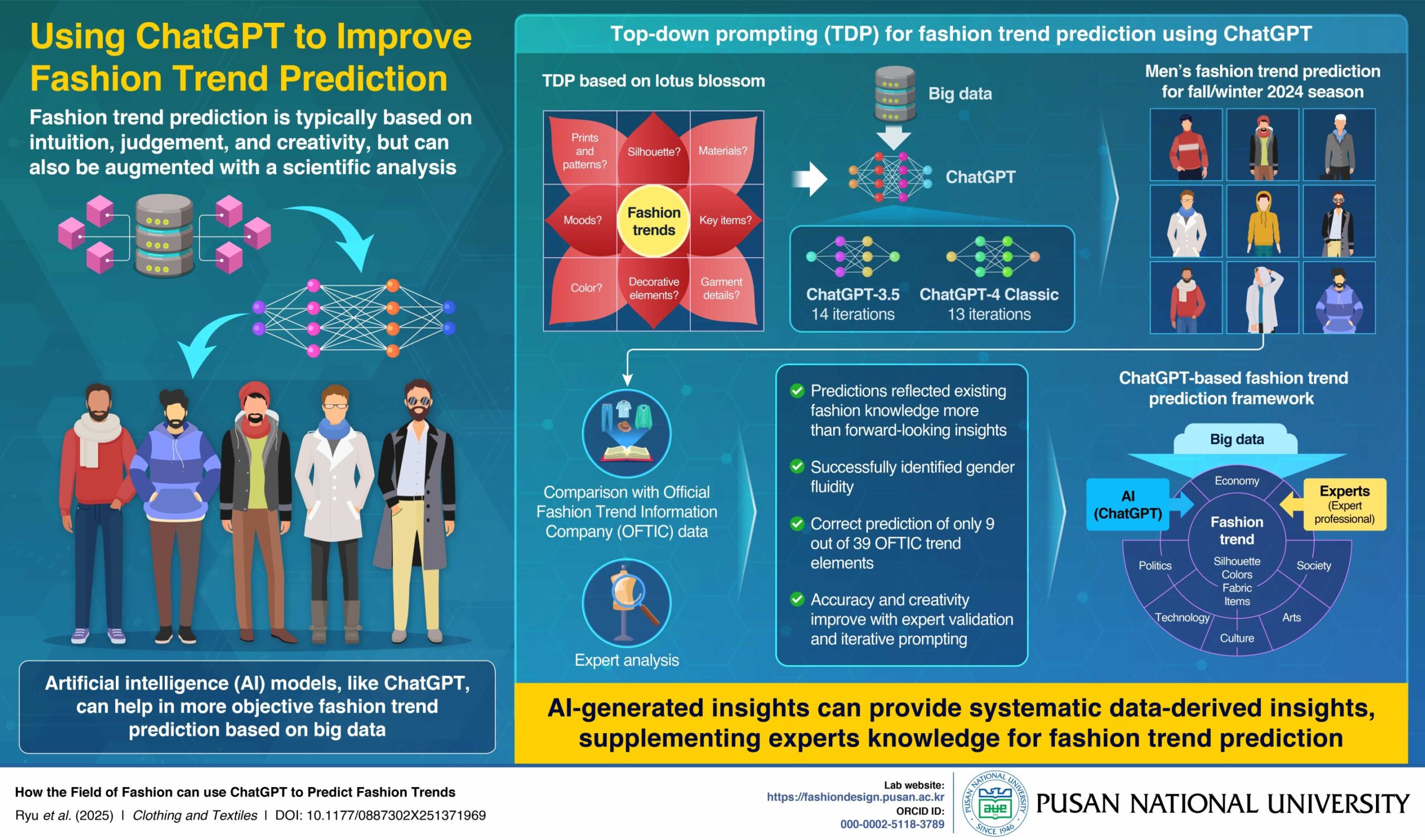
The researchers first verified ChatGPT’s characteristics in fashion trend prediction using general prompts about 2023 fall/winter men’s fashion trends. Based on the results, they developed a new Top-Down Prompting (TDP) technique based on the Lotus Blossom (LB) brainstorming approach, for more accurate and specific forecasting.
TDP starts with a central problem prompt, a general query to predict ‘Fashion Trends’, and then expands into sub-problem prompts, including queries on “Silhouette,” “Materials,” “Key Items,” “Garment Details,” “Decorative Elements,” “Color,” “Moods,” and “Prints and Patterns.”
The researchers used this approach to predict men’s fashion trends for fall/winter 2024 using ChatGPT-3.5 and ChatGPT-4 Classic. The responses were compared and validated against the fall/winter 2024 men’s fashion trend predictions by the Official Fashion Trend Information Company (OFTIC), and the analysis was reviewed by two fashion experts.
Analysis showed that ChatGPT’s predictions mostly reflected established or generalized fashion ideas, rather than forward-looking or innovative designs. Moreover, it accurately identified only nine out of 39 trends predicted in OFTIC’s report. Notably, however, both models predicted emerging themes, including gender fluidity and statement coats.
“While the prediction accuracy of ChatGPT is low, what’s intriguing is that it captured new trends not found in existing data,” notes Dr. Lee. “AI can sense cultural shifts and open up new creative directions.”
Although ChatGPT should not yet be viewed as a definitive forecasting tool, it can effectively complement expert-led analysis. This is especially valuable for fashion students and small brands, helping them achieve more accurate and nuanced trend forecasts. For fashion education, the researchers also developed a TDP-based hybrid conceptual framework for fashion trend forecasting, integrating both AI-analysis and expert-knowledge.
Overall, this study shows how AI tools can make fashion trend forecasting more systematic and accessible.
More information:
Chaehi Ryu et al, How the Field of Fashion can use ChatGPT to Predict Fashion Trends, Clothing and Textiles Research Journal (2025). DOI: 10.1177/0887302×251371969
Provided by
Pusan National University
Citation:
How AI can help predict fashion trends (2025, October 28)
retrieved 28 October 2025
from https://phys.org/news/2025-10-ai-fashion-trends.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.